Windows 11 comes with many new features, one of which is the Windows Subsystem for Android (WSA). Although it means you can technically run your favorite Android apps right on your PC, there is a catch. Microsoft has partnered with Amazon to integrate the Amazon Appstore with the Microsoft Store, which means you can't officially access the Google Play Store's vast library on the native Android subsystem of Windows. To rub salt into the wound, not all Amazon Appstore apps are available on Windows 11 for compatibility reasons.
Luckily, Microsoft ships the Windows Subsystem for Android environment with a working debugging option. As a result, you can access and debug the underlying Android layer from the host Windows 11 OS using the regular Android Debugging Bridge (ADB) binary. Due to the fact that we can use ADB to install any standard Android app installation package (APK), it is also possible to sideload apps on the Windows Subsystem for Android that are not present in the Amazon Appstore.
Sideloading apps on the Windows Subsystem for Android
Keep in mind that the whole Windows Subsystem for Android is a bleeding edge piece of software. The apps curated by Amazon and Microsoft are likely to be heavily optimized for the environment, which is why they managed to secure their seats in the first run. Having said that, many other Android apps should work just fine out of the box. The only way to test the compatibility is to sideload them, and this is where this tutorial will come in handy.
Before beginning, make sure that the WSA instance installed on your PC is up-to-date. If you downloaded it via the Microsoft Store app, the newer versions should be automatically installed in the background. However, for those who downloaded it manually, do install the latest build in the same way.
To sideload any Android app on Windows 11's Subsystem for Android, follow these steps:
- Download the APK file of your desired app or game from a trusted source. Keep in mind that you don't have to stick with the x86(-64) variant of the APK, as WSA can emulate native Arm(64) apps on x86 platforms, thanks to Intel Bridge Technology. Having said that, if you have a Windows on Arm laptop, then always choose the Arm(64) APK for optimal performance.
- If it's a community-developed project, check out the respective thread on XDA forums or similar platforms.
- APKs of open source apps are often found through their GitHub repo, or on stores like F-Droid as well.
- There are third-party APK hosting resources like APK Mirror and APKPure, which are worth looking for.
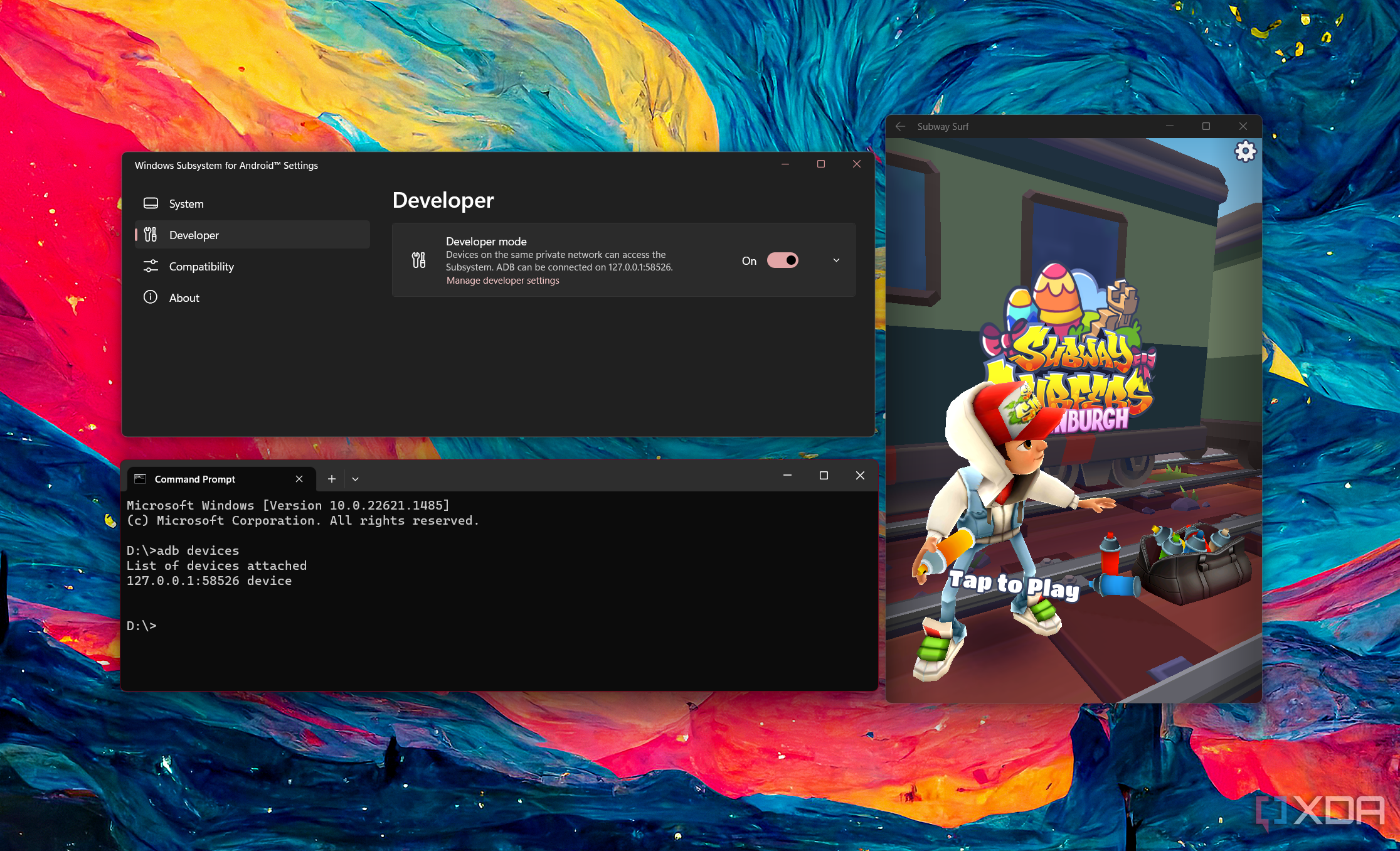
- Once you have your hands on the APK file, start the Windows Subsystem for Android environment. Click on the Start Menu, then click on the All apps button, and locate the shortcut named Windows Subsystem for Android. You can also type "subsystem" in the search box to make it quicker.
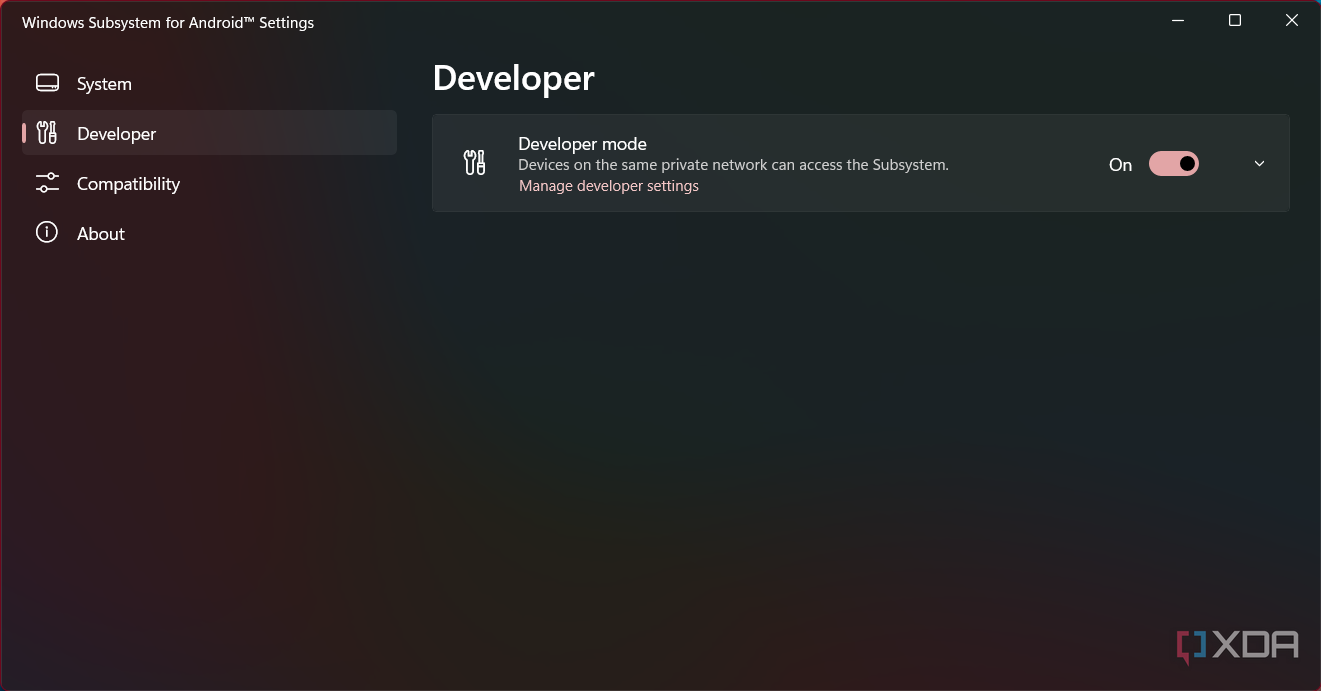
- You should see the Windows Subsystem for Android settings screen. Go to the Developer tab on the left pane and enable the Developer mode option.
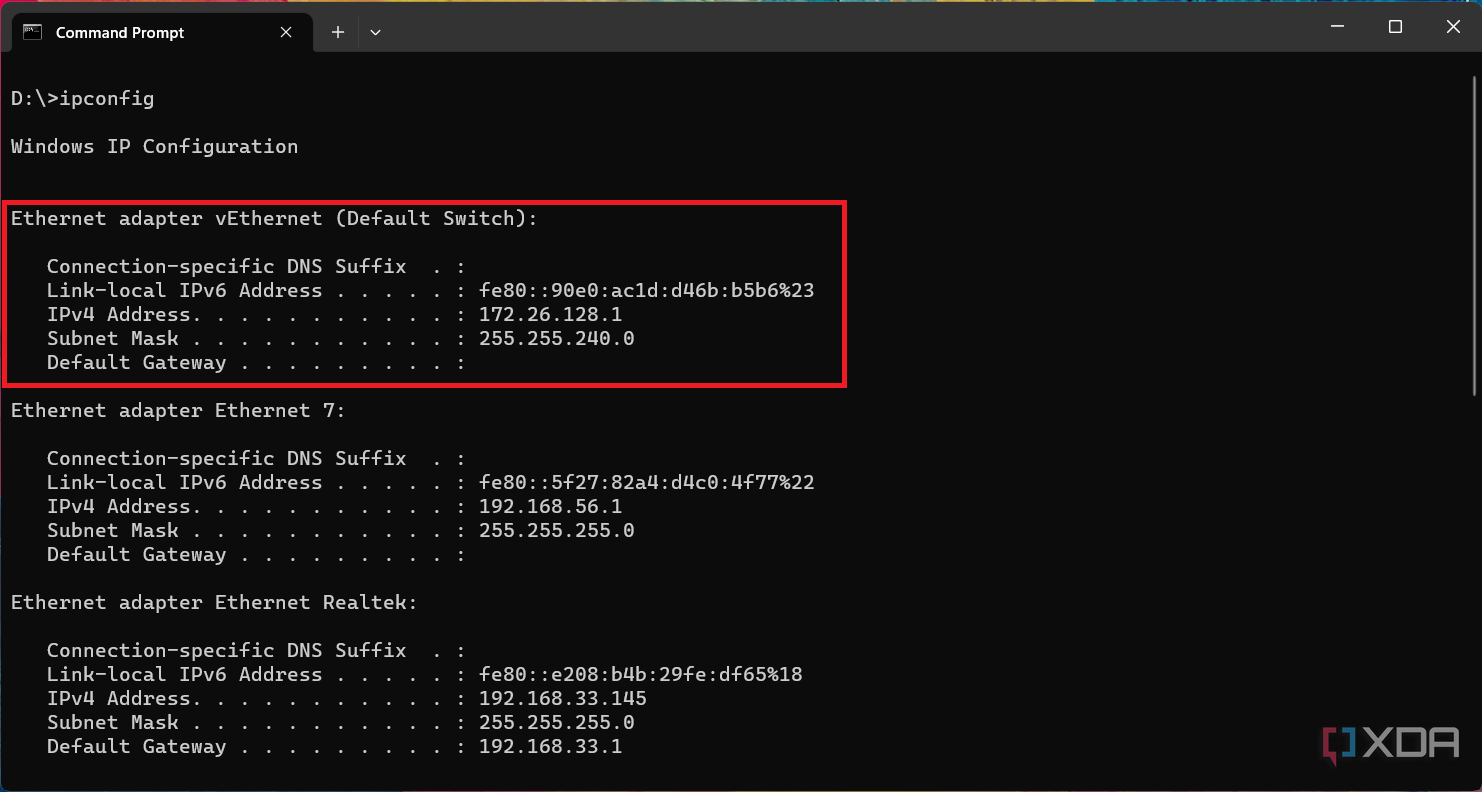
- Since this particular Android instance is running alongside the host Windows kernel, we can access it through the localhost (127.0.0.1) interface. In fact, the Android layer also binds itself to a random IP from the 172.30.0.0/24 private network, which can be seen from the
ipconfigoutput under the "Ethernet adapter vEthernet (Default Switch)" section. - As soon as the Android layer is running, we can connect it using ADB from the host Windows 11 OS. You can either use the localhost (127.0.0.1) with port 58526, or the IP address shown in the
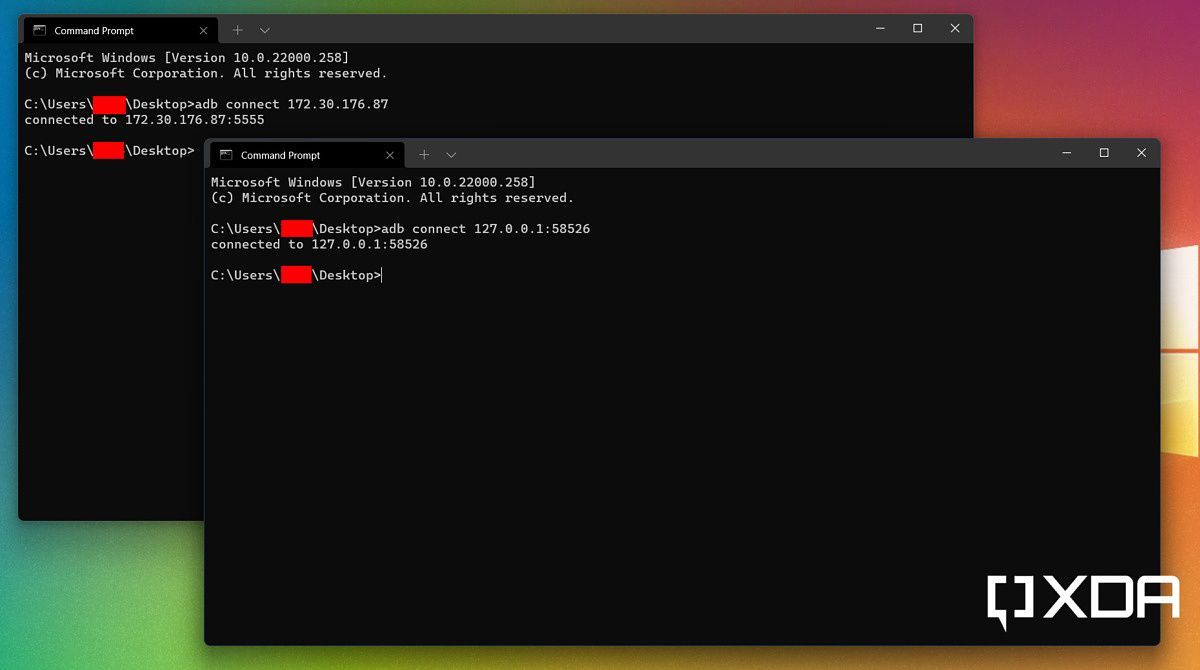
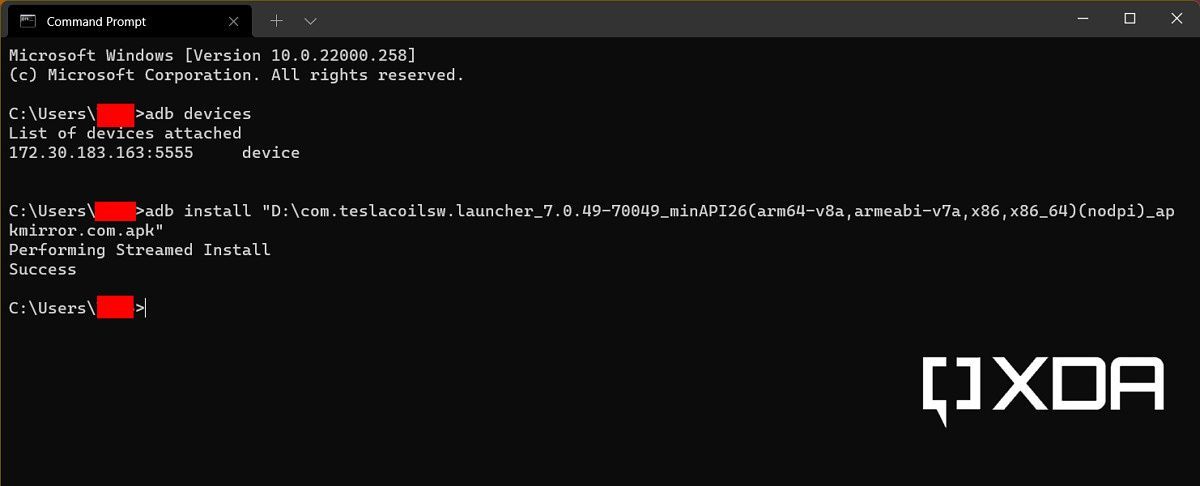
ipconfigoutput to establish the connection. Assuming you've set up ADB to use it from any location on your PC, open a new Windows Terminal window and type one of the following:adb connect 127.0.0.1:58526adb connect <IP address>:58526 - Now we can install our desired APK through ADB. The command should be as follows:
adb install <full_path_to_the_APK_file>If your desired app is available as an app bundle like AAB/APKS/APKM/XAPK instead of the regular APK file, then take a look at our Android app sideloading tutorial to install it. - If everything goes right, then a shortcut to the Android app will be created under the Start Menu of Windows - just like any regular Windows app. Click on the shortcut to start the app.
- In case you can't find the shortcut of the Android app, you can manually run it using the following command:
%LOCALAPPDATA%\Microsoft\WindowsApps\MicrosoftCorporationII.WindowsSubsystemForAndroid_8wekyb3d8bbwe\WsaClient.exe /launch wsa://<PACKAGENAME>%LOCALAPPDATA%\Microsoft\WindowsApps\MicrosoftCorporationII.WindowsSubsystemForAndroid_8wekyb3d8bbwe\WsaClient.exe /launch wsa://com.kiloo.subwaysurf - You can also invoke the app directly from a connected ADB shell window:
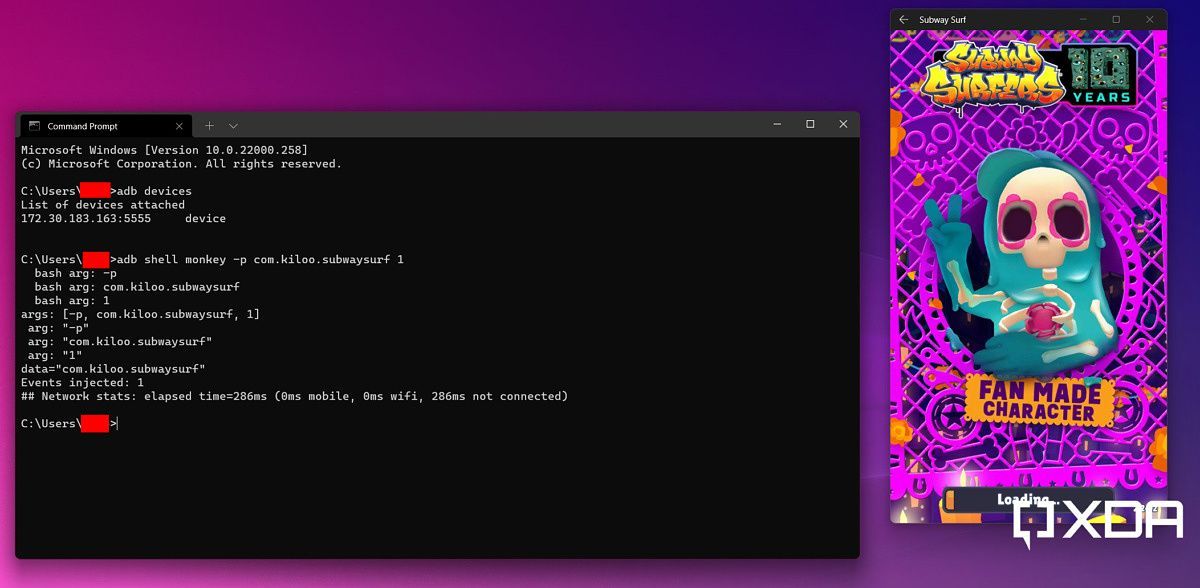
adb shell monkey -p <PACKAGENAME> 1adb shell monkey -p com.kiloo.subwaysurf 1 - Another simple way to access the sideloaded apps is installing a launcher on Windows Subsystem for Android.
- In case you can't find the shortcut of the Android app, you can manually run it using the following command:
There exist third-party GUI wrappers such as WSATools that offer similar functionalities. With that said, understanding the basics would be handy, especially if you're a developer or someone who just wants to know how things work under the hood.
The sideloaded apps will have network access, which means you can install and use the Android variant of popular browsers like Firefox inside the Windows Subsystem for Android, and then use that for downloading apps straight away. Windows 11 also lets you apply firewall rules on Android apps. While it is possible to sideload an app that relies on Google services, it'll crash while attempting to run it due to the lack of Google services, unless you install a modifed WSA with Google Play or use microG as a possible workaround.
And there we are. Now you can summon WSA with your own choice of apps. After getting accustomed to sideloading Android apps in Windows 11, take a look at how to use a package manager for WSA. We also have lots of other Windows and Android guides, so consider getting to grips with how to transfer files between Android and Windows PC.